leetcode探索之队列 & 栈学习 队列:先入先出的数据结构
作者:whisper
链接:http://proprogrammar.com:443/article/592
声明:请尊重原作者的劳动,如需转载请注明出处
本章节中,我们将首先介绍先入先出(FIFO)及其在队列中的工作方式。
本章的目的是帮助你:
- 理解 FIFO 和队列的定义;
- 能够自己实现队列;
- 熟悉内置队列结构;
- 使用队列来解决简单的问题。
先入先出的数据结构
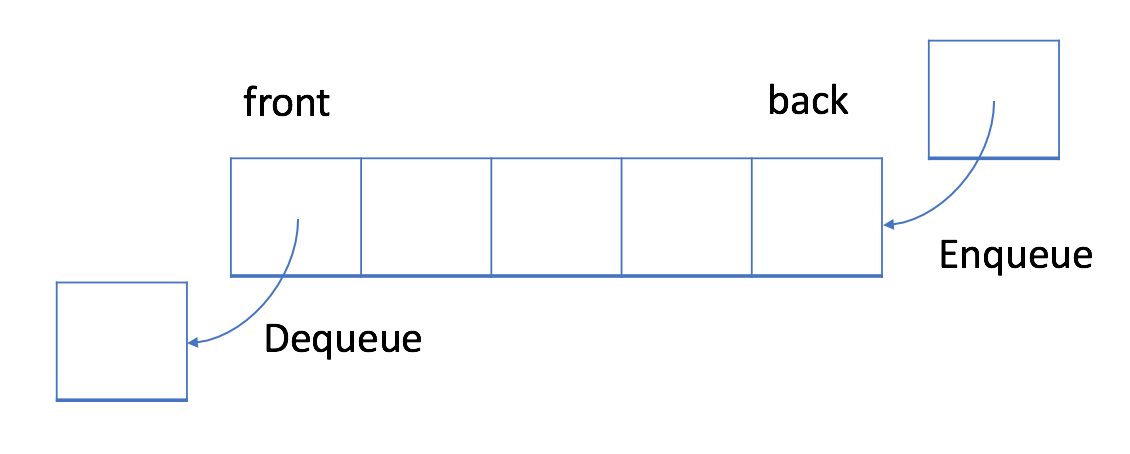
在 FIFO 数据结构中,将首先处理添加到队列中的第一个元素。
如上图所示,队列是典型的 FIFO 数据结构。插入(insert)操作也称作入队(enqueue),新元素始终被添加在队列的末尾。 删除(delete)操作也被称为出队(dequeue)。 你只能移除第一个元素。
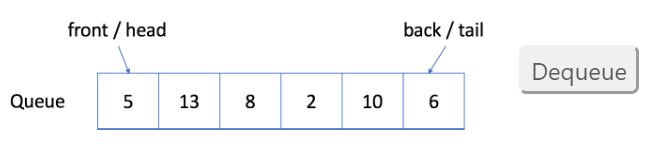
示例 - 队列
1. 入队:您可以单击下面的 Enqueue 以查看如何将新元素 6 添加到队列中。

2. 出队:您可以单击下面的 Dequeue 以查看将删除哪个元素。
队列 - 实现
为了实现队列,我们可以使用动态数组和指向队列头部的索引。
如上所述,队列应支持两种操作:入队和出队。入队会向队列追加一个新元素,而出队会删除第一个元素。 所以我们需要一个索引来指出起点。
这是一个供你参考的实现:
// "static void main" must be defined in a public class.
class MyQueue {
// store elements
private List<Integer> data;
// a pointer to indicate the start position
private int p_start;
public MyQueue() {
data = new ArrayList<Integer>();
p_start = 0;
}
/** Insert an element into the queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean enQueue(int x) {
data.add(x);
return true;
};
/** Delete an element from the queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean deQueue() {
if (isEmpty() == true) {
return false;
}
p_start++;
return true;
}
/** Get the front item from the queue. */
public int Front() {
return data.get(p_start);
}
/** Checks whether the queue is empty or not. */
public boolean isEmpty() {
return p_start >= data.size();
}
};
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueue q = new MyQueue();
q.enQueue(5);
q.enQueue(3);
if (q.isEmpty() == false) {
System.out.println(q.Front());
}
q.deQueue();
if (q.isEmpty() == false) {
System.out.println(q.Front());
}
q.deQueue();
if (q.isEmpty() == false) {
System.out.println(q.Front());
}
}
}缺点
上面的实现很简单,但在某些情况下效率很低。 随着起始指针的移动,浪费了越来越多的空间。 当我们有空间限制时,这将是难以接受的。
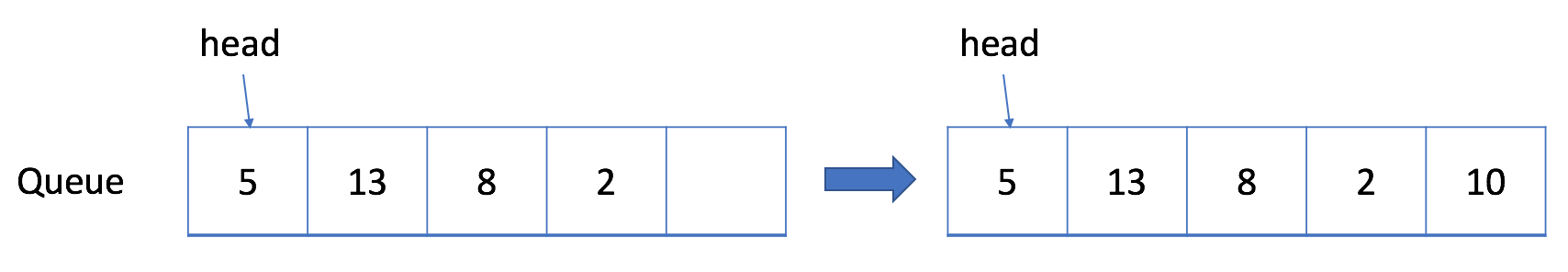
让我们考虑一种情况,即我们只能分配一个最大长度为 5 的数组。当我们只添加少于 5 个元素时,我们的解决方案很有效。 例如,如果我们只调用入队函数四次后还想要将元素 10 入队,那么我们可以成功。
但是我们不能接受更多的入队请求,这是合理的,因为现在队列已经满了。但是如果我们将一个元素出队呢?
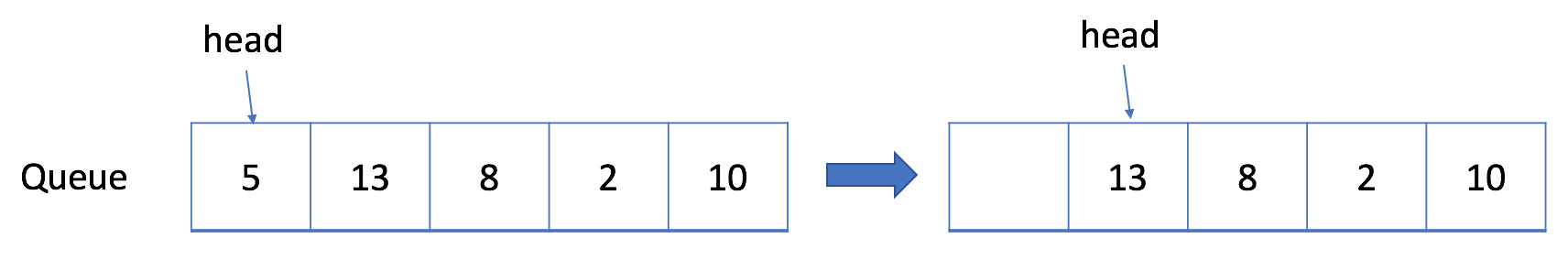
实际上,在这种情况下,我们应该能够再接受一个元素。
循环队列
此前,我们提供了一种简单但低效的队列实现。
更有效的方法是使用循环队列。 具体来说,我们可以使用固定大小的数组和两个指针来指示起始位置和结束位置。 目的是重用我们之前提到的被浪费的存储。
让我们通过一个示例来查看循环队列的工作原理。 你应该注意我们入队或出队元素时使用的策略。
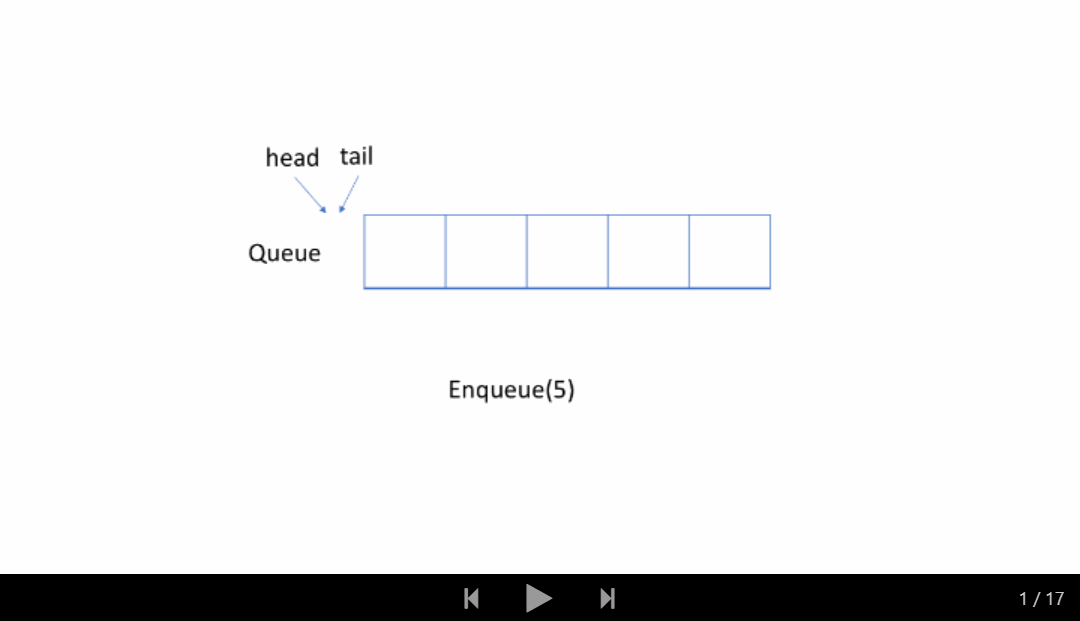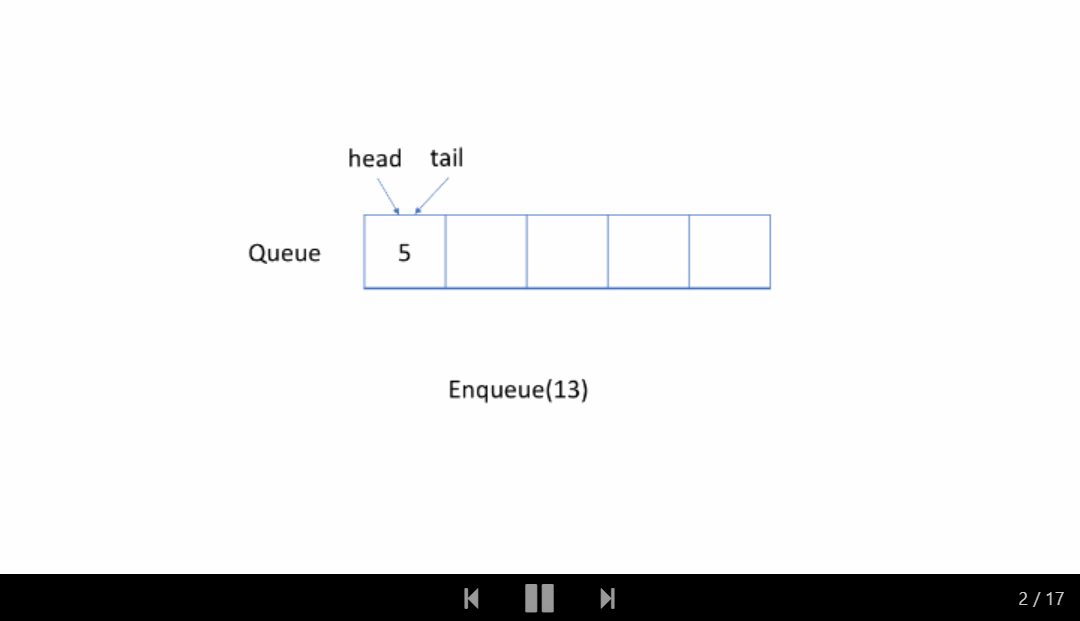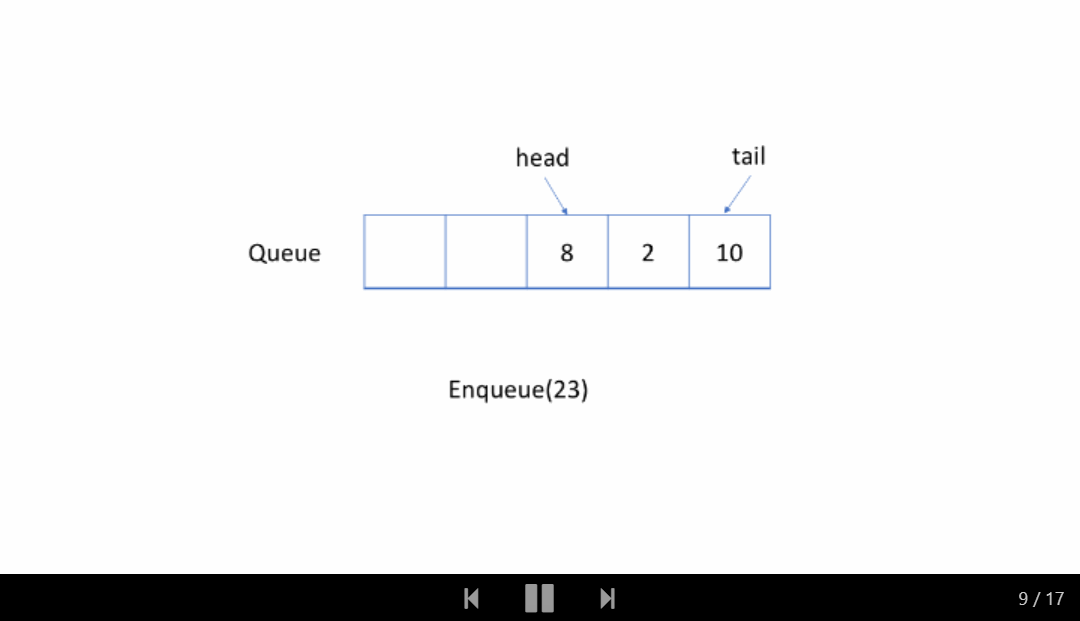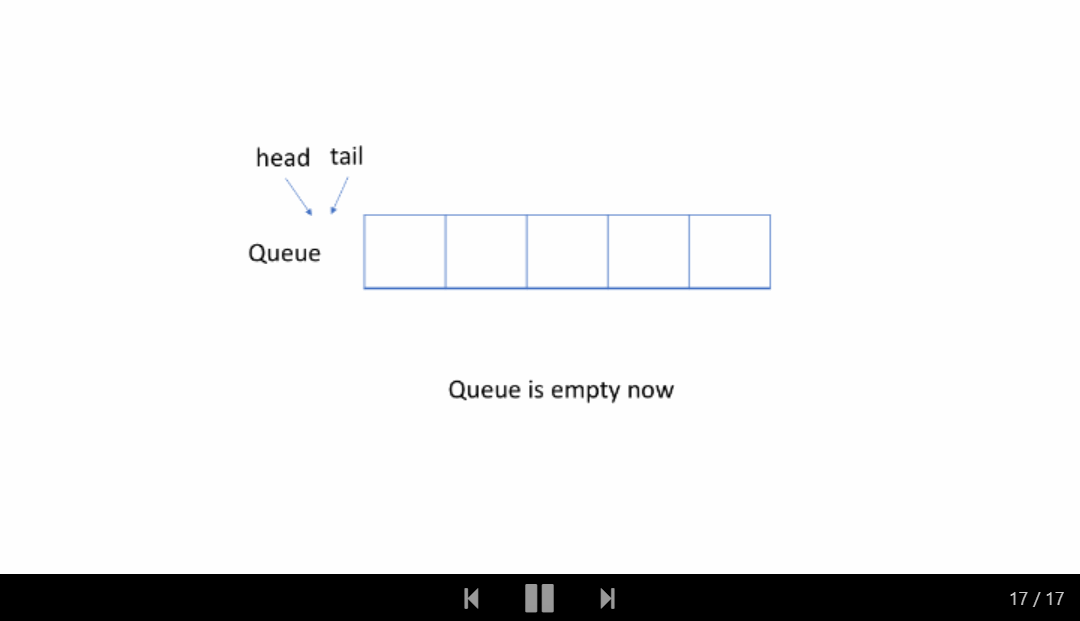
仔细检查动画,找出我们用来检查队列是空还是满的策略。
下一个练习,我们将让你自己尝试实现循环队列,之后会提供给你一个解决方案。
算法-设计循环队列
设计你的循环队列实现。 循环队列是一种线性数据结构,其操作表现基于 FIFO(先进先出)原则并且队尾被连接在队首之后以形成一个循环。它也被称为“环形缓冲器”。
循环队列的一个好处是我们可以利用这个队列之前用过的空间。在一个普通队列里,一旦一个队列满了,我们就不能插入下一个元素,即使在队列前面仍有空间。但是使用循环队列,我们能使用这些空间去存储新的值。
你的实现应该支持如下操作:
- MyCircularQueue(k): 构造器,设置队列长度为 k 。
- Front: 从队首获取元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
- Rear: 获取队尾元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
- enQueue(value): 向循环队列插入一个元素。如果成功插入则返回真。
- deQueue(): 从循环队列中删除一个元素。如果成功删除则返回真。
- isEmpty(): 检查循环队列是否为空。
- isFull(): 检查循环队列是否已满。
示例:
MyCircularQueue circularQueue = new MycircularQueue(3); // 设置长度为 3 circularQueue.enQueue(1); // 返回 true circularQueue.enQueue(2); // 返回 true circularQueue.enQueue(3); // 返回 true circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 false,队列已满 circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 3 circularQueue.isFull(); // 返回 true circularQueue.deQueue(); // 返回 true circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 true circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 4提示:
- 所有的值都在 0 至 1000 的范围内;
- 操作数将在 1 至 1000 的范围内;
- 请不要使用内置的队列库。
class MyCircularQueue {
int front, rear;
int[] data;
int size;
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
data = new int[k];
front = 0;
rear = 0;
size = 0;
}
/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(size == data.length){
return false;
}else{
data[rear] = value;
rear = (rear+1)%data.length;
size++;
}
return true;
}
/** Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean deQueue() {
if(size == 0){
return false;
}else{
front = (front+1)%data.length;
size--;
}
return true;
}
/** Get the front item from the queue. */
public int Front() {
if(size == 0){
return -1;
}
return data[front];
}
/** Get the last item from the queue. */
public int Rear() {
if(size == 0){
return -1;
}
return data[(data.length + rear - 1)%data.length];
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */
public boolean isFull() {
return size == data.length;
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularQueue obj = new MyCircularQueue(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.enQueue(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.deQueue();
* int param_3 = obj.Front();
* int param_4 = obj.Rear();
* boolean param_5 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_6 = obj.isFull();
*/用数组存储数据,定义队首,队尾,用size定义队列大小,入队出队进行取余操作
size其实可以省掉,用front,rear的关系确定当前队列中元素的数量,rear == front时为空,(rear + data.length - front) % data.length == data.length - 1时为满
循环队列 - 实现
在循环队列中,我们使用一个数组和两个指针(head 和 tail)。 head 表示队列的起始位置,tail 表示队列的结束位置。
这里我们提供了代码供你参考:
class MyCircularQueue {
private int[] data;
private int head;
private int tail;
private int size;
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
data = new int[k];
head = -1;
tail = -1;
size = k;
}
/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if (isFull() == true) {
return false;
}
if (isEmpty() == true) {
head = 0;
}
tail = (tail + 1) % size;
data[tail] = value;
return true;
}
/** Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean deQueue() {
if (isEmpty() == true) {
return false;
}
if (head == tail) {
head = -1;
tail = -1;
return true;
}
head = (head + 1) % size;
return true;
}
/** Get the front item from the queue. */
public int Front() {
if (isEmpty() == true) {
return -1;
}
return data[head];
}
/** Get the last item from the queue. */
public int Rear() {
if (isEmpty() == true) {
return -1;
}
return data[tail];
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == -1;
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */
public boolean isFull() {
return ((tail + 1) % size) == head;
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularQueue obj = new MyCircularQueue(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.enQueue(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.deQueue();
* int param_3 = obj.Front();
* int param_4 = obj.Rear();
* boolean param_5 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_6 = obj.isFull();
*/队列 - 用法
大多数流行语言都提供内置的队列库,因此您无需重新发明轮子。
如前所述,队列有两个重要的操作,入队 enqueue 和出队 dequeue。 此外,我们应该能够获得队列中的第一个元素,因为应该首先处理它。
下面是使用内置队列库及其常见操作的一些示例:
// "static void main" must be defined in a public class.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. Initialize a queue.
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList();
// 2. Get the first element - return null if queue is empty.
System.out.println("The first element is: " + q.peek());
// 3. Push new element.
q.offer(5);
q.offer(13);
q.offer(8);
q.offer(6);
// 4. Pop an element.
q.poll();
// 5. Get the first element.
System.out.println("The first element is: " + q.peek());
// 7. Get the size of the queue.
System.out.println("The size is: " + q.size());
}
}算法-数据流中的移动平均值
给定一个整数数据流和一个窗口大小,根据该滑动窗口的大小,计算其所有整数的移动平均值。
示例:
MovingAverage m = new MovingAverage(3); m.next(1) = 1 m.next(10) = (1 + 10) / 2 m.next(3) = (1 + 10 + 3) / 3 m.next(5) = (10 + 3 + 5) / 3
class MovingAverage {
// 保存最近size个数的和
double sum;
// 窗口的size
int size;
// 保存窗口的元素
Queue<Integer> q;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MovingAverage(int size) {
q = new LinkedList<>();
this.size = size;
sum = 0;
}
public double next(int val) {
if(q.size() < size){
q.offer(val);
}else{
sum -= q.poll();
q.offer(val);
}
sum += val;
return sum / q.size();
}
}
/**
* Your MovingAverage object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MovingAverage obj = new MovingAverage(size);
* double param_1 = obj.next(val);
*/上面是用语言内置的队列,下面是自己用数组实现的队列,效率高一些
class MovingAverage {
int[] queue;
int headerIndex;
int count;
int size;
int sum;
MovingAverage(int size){
this.size = size;
queue = new int[size];
// headerIndex = -1;
}
public double next(int value){
if (size == count) {
// todo:
sum -= queue[headerIndex];
headerIndex = (headerIndex + 1) % size;
count--;
}
int tailIndex = (headerIndex + count) % size;
queue[tailIndex] = value;
sum += value;
count++;
return (double) sum/count;
}
}
/**
* Your MovingAverage object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MovingAverage obj = new MovingAverage(size);
* double param_1 = obj.next(val);
*/
亲爱的读者:有时间可以点赞评论一下
作者其它文章
- 数字图像处理
- 剑指offer2
- 工作学习
- 这些算法有自己的方法
- 插件
- 软件使用
- 数学
- mybatis
- 计算机网络
- 正则表达式专栏
- 问题记录
- Thymeleaf
- zuul
- hystrix
- 正则表达式
- feign
- 编程相关技术
- ribbon
- 微服务
- eureka
- 分布式
- 模板
- angularjs
- javascript
- html
- c++ grammar
- c grammar
- python grammar
- java grammar
- 软件工程
- 数据库系统概论
- 转载
- 小知识
- 考研
- webservice
- 网络
- struts2
- springmvc
- springboot
- redis
- mongodb
- hibernate
- 计算机组成原理
- 当代世界经济与政治
- leetcode
- 思想道德修养与法律基础
- 毛泽东思想和中国特色社会主义理论体系概论
- 作乐
- 生活点滴
- 娱乐
- 中国近现代史纲要
- 操作系统
- sunny day, singing day
- 设计模式与算法
- 框架
- 概率论与数理统计
- 线性代数
- JAVA
- 前端
- 数据库
- 马克思主义基本原理概论
- 软考
- 生活,生,活
- 晴雨
- CSS
- LINUX
- java web整合开发王者归来
- 英语
- 高等数学
- 数据结构
















全部评论